Finally, let us show how the Faceted Query Engine handles queries that involve aggregation. As an example, suppose we wish to find the combined weight of all ![]() Pottery per
Pottery per ![]() Layer. We start by aggregating the entity set
Layer. We start by aggregating the entity set ![]() Pottery by weight.
Pottery by weight.
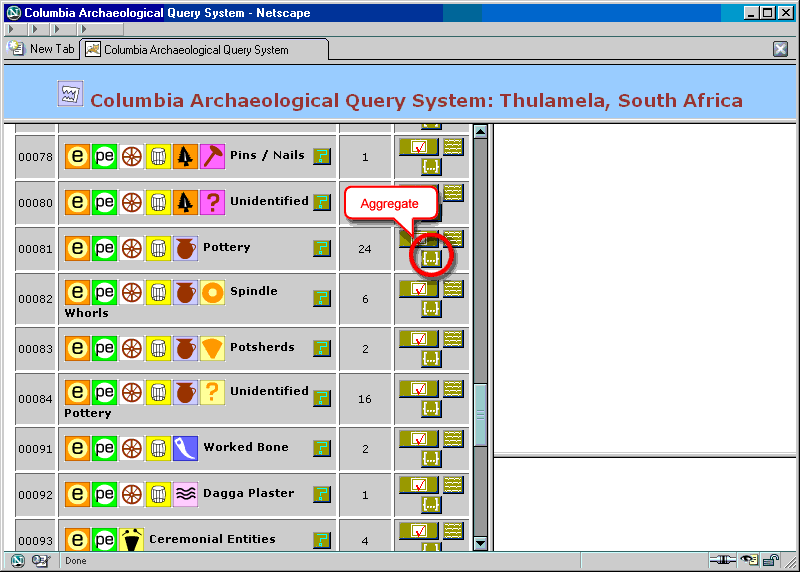
Figure 21. Aggregation: choosing entity set
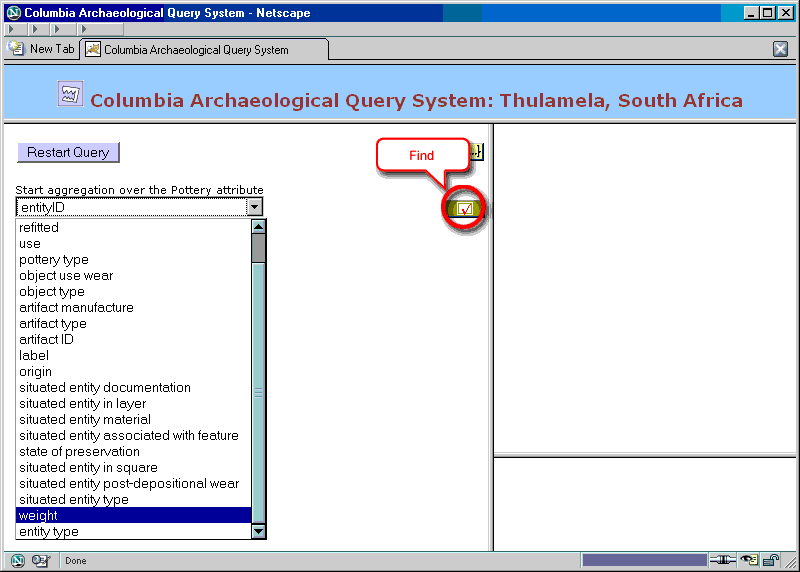
Figure 22. Aggregation: choosing attribute
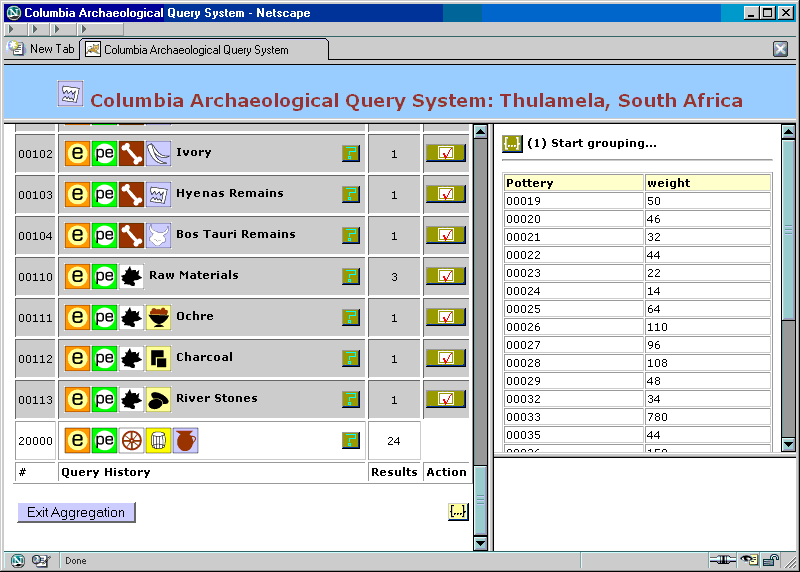
Figure 23. Aggregation: inspecting attribute values
We then proceed to relate the new aggregate entity set to the entity set ![]() Layers, in a manner similarly to section 5.4.
Layers, in a manner similarly to section 5.4.
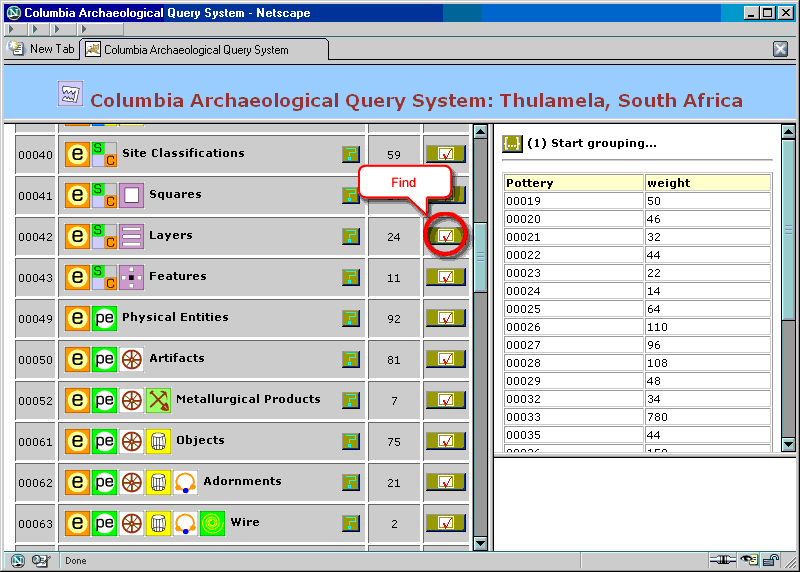
Figure 24. Aggregation: choosing a related entity set
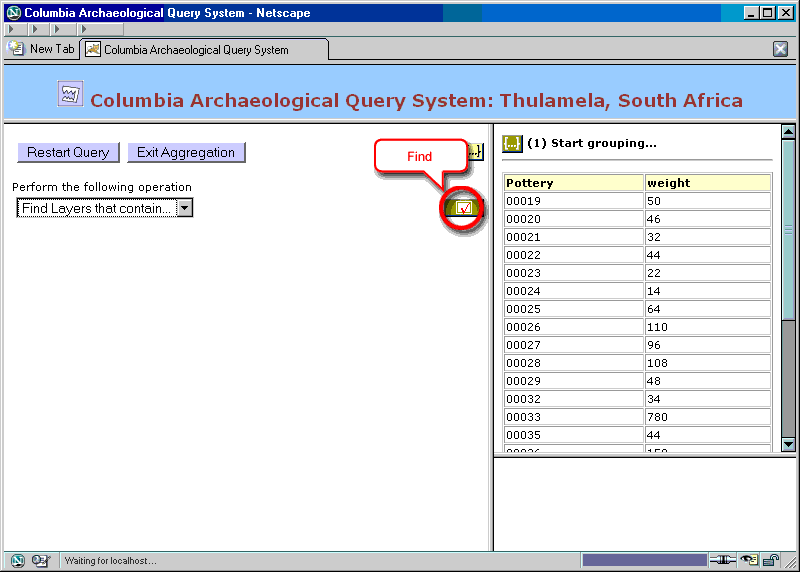
Figure 25. Aggregation: relating entity sets (step 1)
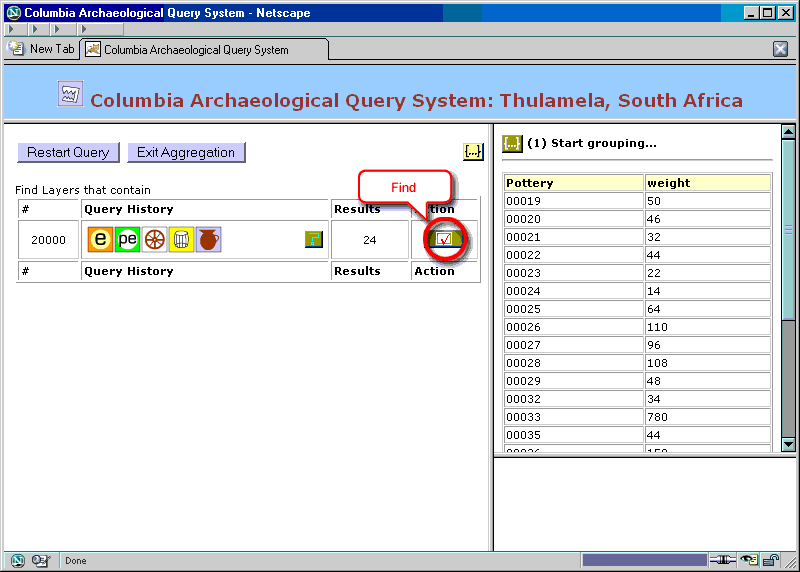
Figure 26. Aggregation: relating entity sets (step 2)
We save the new entity set, ![]() Layers with Pottery, and start aggregation.
Layers with Pottery, and start aggregation.
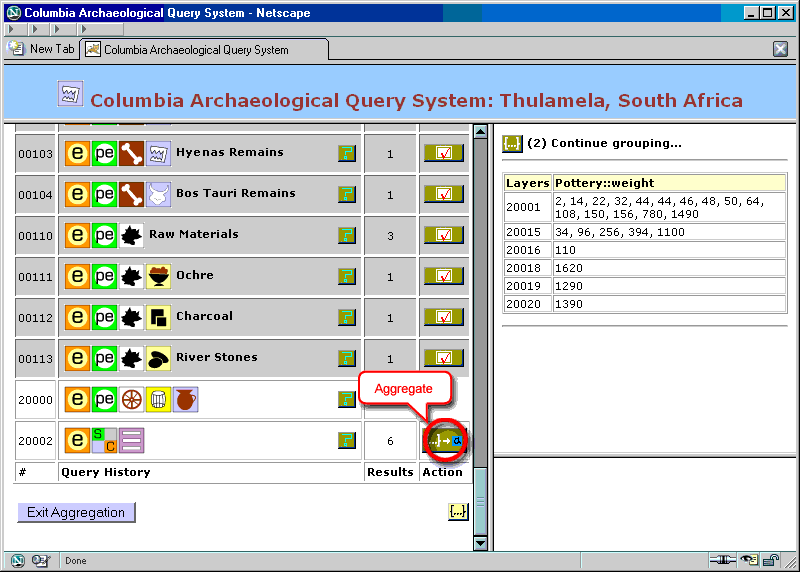
Figure 27. Aggregation: inspecting intermediate results
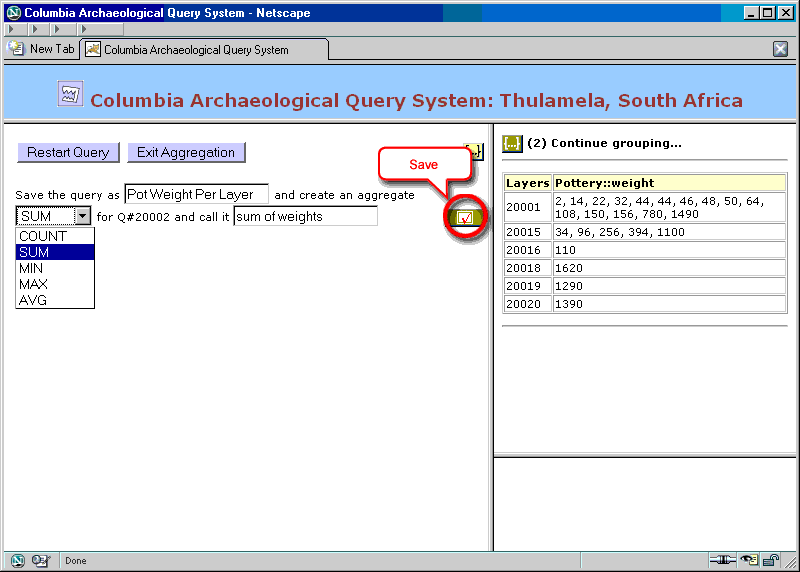
Figure 28. Aggregation: choosing aggregate function
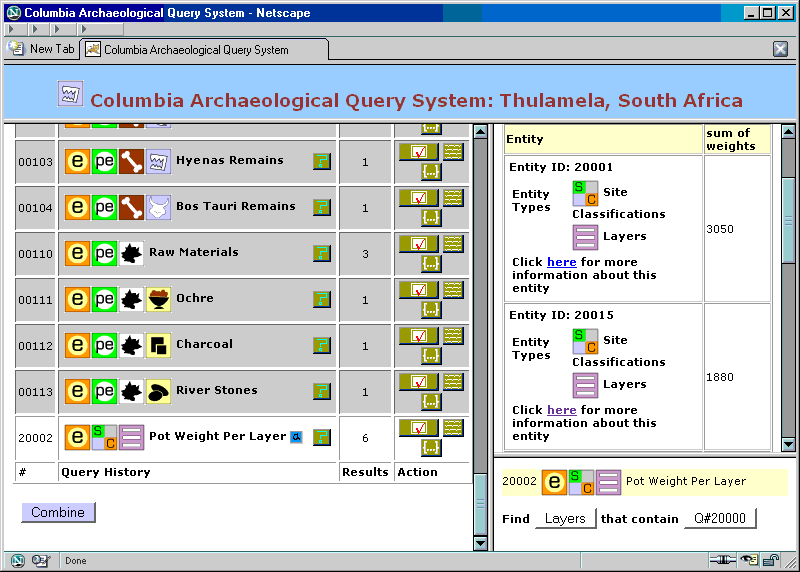
Figure 29. Aggregation: inspecting and saving query results
There are 6 ![]() Layers with Pottery, and the combined weight of pottery per layer are displayed in the Detail window.
Layers with Pottery, and the combined weight of pottery per layer are displayed in the Detail window.
© Internet Archaeology
URL: http://intarch.ac.uk/journal/issue21/3/aggregation.html
Last updated: Mon April 30 2007