Muscle tissue
Biological description
- There are three main types of muscle tissue in animals: smooth, cardiac, and skeletal (Martini 2005, 236). Smooth muscle cells are spindle-shaped, non-striated, and uni-nuclear. Cardiac muscle cells are striated, branched, and uni-nucleated. Skeletal muscle cells are striated, tubular, and multi-nucleated. Skeletal muscle makes up the majority of muscle mass in an animal and is under voluntary control.
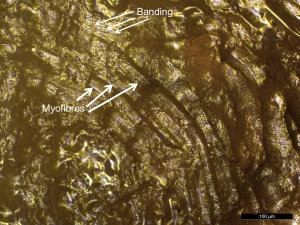
- The muscle fibre, or myofibre, is the basic unit of skeletal muscle (Stocum 2012, 127). Myofibres are long and range in size from less than 100 μm wide and a few millimetres long to several hundred microns wide and a few centimetres long (Lieber 2009), depending on where the muscle is located in the body. A myofibre contains many long smaller structures called myofibrils that run the length of the myofibre (Clark 2005, 143). Myofibrils are in turn composed of thick, thin, and elastic myofilaments, arranged into repeating subunits called sarcomeres. The arrangement of the sarcomeres results in the appearance of cross striations on the myofibre, seen as a dark and light banding pattern with VLM (Lieber and Fridén 1991, 691).
Identification
- Myofibres must display banding, reflecting the ordered arrangement of the sarcomeres within the myofibre, to identify striated muscle tissue residue.
- The reference beef muscle residue was dried but still in a relatively fresh state, and long myofibres with banding cross striations were visible. However, no visually diagnostic traits were present within any buried and aged muscle tissues on flint. Thus, it seems very unlikely that morphological features of muscle residues on stone tools would be preserved in most archaeological circumstances.
Identification notes
- When micrographs of gelatinous hyphae and muscle tissue residue are compared, they are indistinguishable, both appearing as networks of translucent fibres containing holes that can sometimes display birefringence (Langejans 2009, 171, 285, 292, 400).
Reference residue
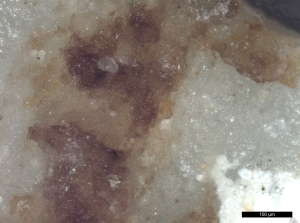
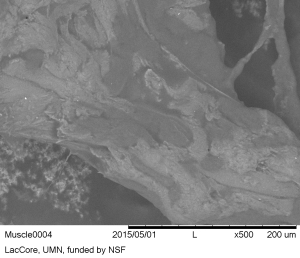
- Myofibres with cross striations or banding patterns characteristic of striated muscle (Kenyon 2012, 1273), were sometimes visible with reflected VLM in the reference beef muscle residue (Figure 40). Surprisingly, the distinctive banding seen within the myofibre structure with VLM, was not found in the SEM images taken even at 500x (see Figure 41).
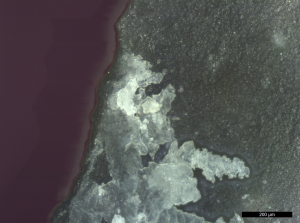
- No beef muscle myofibres with banding were found on any flint pieces buried in the experiment. After burial in the wetland for 1 month, suspected muscle tissue was devoid of colour and appeared as a translucent fibrous sheet with holes (see Figure 42). However, these traits are not specific to muscle.

Bone
Biological description
- Bone is a complex composite material. Mature compact bone is composed of approximately 70% carbonate hydroxylapatite (bone mineral) and 30% Type 1 collagen (protein) (Monnier et al. 2012, 3291). Patterning reflective of structure is present in different types of bone, and these patterns are potentially observable. However, these patterns are only visible when the sample is prepared and viewed along the correct plane or axis, and viewed with transmitted light microscopy or SEM.
- Currey (2008, 6–8) defines four types of bone that display characteristics visible with SEM: 1) lamellar bone, 2) woven bone, 3) fibrolamellar bone, 4) secondary osteons (Haversian systems).
Identification
- On histological transverse thin sections (cross sections), it is possible to differentiate between bone, antler, and ivory (Anderson 1980, 190). However when viewed as in situ residues on stone tools, no distinction can confidently be made between possible bone and antler residues if both are expected to occur within the geographic area being studied archaeologically, since antler is also mostly composed of carbonate hydroxylapatite. In compact bone, the features of osteon units are visible only in prepared cross thin sections when viewed with a transmitted light microscope or SEM, not with the reflected VLM used in this study. The visible features of the osteon include concentric bone lamellae surrounding Haversian canals and several osteocytes with branched canaliculi (Jans 2005, 7; Rhinelander 1972, 7; White and Folkens 2005, 43). Spongy or cancellous bone does not contain osteons; however, osteocytes composing the bony trabeculae are arranged in a lacunar-canalicular system similar to compact bone (Eurell 2004, 17). Canaliculi openings on the surface of spongy bone are visible in histological preparations.
- According to Lombard (2008, 38), bone fragments have sharp jagged edges that may show perforations at magnifications over 200x. Langejans (2009, 64) and Langejans and Lombard (2015, 207) describe bone and fatty bone deposits on experimental tools as amorphous, opaque, non-birefringent, and having no characteristic structure, but state that angular bone flakes are identifiable.
- Fresh scraped bone exhibits a characteristic white colour, angular shapes, and has opaque to translucent portions, but no features with a distinctive morphology that can be used to make a secure identification with reflected VLM. Furthermore, when bone begins to degrade, the colour, translucency, and shape may also be altered.
Identification notes
- Cortical bone is semi-crystalline in structure due to apatite crystals that form around collagen fibrils in ordered layers. Bone, and sometimes degraded bone, displays extinction crosses when prepared as a histological sample on a glass slide, with the osteons cut in cross section and viewed under polarised light with a transmitted light microscope (Jans 2005). However, bone fragment residues are never encountered in this particular orientation on lithic tools. Even if by chance a cross-sectional cut through osteons were encountered during reflected VLM examination of in situ residues, the maltese crosses would probably fail to be recognised since birefringent qualities of anisotropic residues are only weakly visible while being viewed in situ.
Reference residue
- Bone flakes observed in the reference collection appear as angular crystal pieces, ranging in colour from taupe brown to white to translucent (Figure 43).
- When viewed in situ on stone with reflected VLM, bone residue fragments can appear similar to small minerals. For instance, within the blank flint, angular and rectangular linearly arranged crystal inclusions were observed (see Figures 15 and 16) that appear similar to experimentally produced bone residues. Non-bone white flint crystals were also found at the edge of used flakes from stone attrition resulting from tool use.
- Secure identification of tiny bone residue fragments located in situ on a stone tool is not possible, as the distinguishing morphological features present in cortical bone are invisible when viewed using reflected VLM. Extraction from the artefact and viewing on slides is also unlikely to orient thin cortical bone fragments by random chance in the cross-sectional plane required to allow location of features.
- SEM viewing of in situ bone residues in the reference collection does not appear to improve characterisation (Figure 44); this agrees with SEM observations of experimental bone residues on stone by Jahren et al. (1997, 248).
- No osteons were observed in the SEM micrographs. Bone fragments appeared angular and jagged, similar to the reflected VLM observations.

Antler
Biological description
- Antlers are paired branched cranial appendages found in the Cervidae family (deer, moose, elk, caribou and reindeer) (Hall 2005, 103).
- Antlers are dead ossified tissue that is deciduous (usually shed annually) and regenerates. This is in contrast to horns, which are living permanent tissues mostly composed of keratin.
- The antler growth cycle in male deer and reindeer has been strongly correlated with the concentration of testosterone in the blood (Bubenik et al. 1997, 269; Kierdorf et al. 2003, 741; Muir et al. 1988, 31).
- Antler is primarily composed of bone covered with epithelial velvet for part of each year.
Identification
- Prepared histological cross sections of antler, like bone, reveal osteons and trabecular bone tissue (Landete-Castillejos et al. 2012, 248). However, the structure of the osteons could not be located in the reference antler residues on stone tools. Thus, antler residues were considered amorphous with no distinct structure.
- Antler residues were white to light brown and composed of angular flakes with jagged edges. Many soil minerals also share the same general appearance.
Reference residue
- Since antler is mainly composed of bone, it is no surprise that it is indistinguishable from bone microscopically, with jagged crystalline pieces of a light brown to translucent colour (Figure 45). The edges of pieces sometimes appear 'frayed'. Occasionally irregular elongate or somewhat fibrous antler pieces can be seen. As with bone residues, antler residues could also be mistaken for minerals.
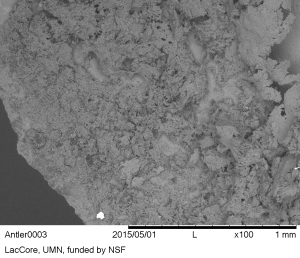
- During SEM viewing, the antler residue appeared more fibrous and net-like than the bone residues, but still contained angular fragments (Figure 46).

Blood films
Biological description
- Blood contains four major components: red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), platelets (thrombocytes), and plasma (the liquid portion), but it is the red blood cells that have been reported as being identifiable microscopically on ancient stone tools by a number of archaeologists (Kononenko et al. 2016; Lombard 2008; 2011; 2014; Loy 1983; Loy and Dixon 1998; Loy and Hardy 1992; Robertson et al. 2009; Williamson 2004).
- The membranes of red blood cells (RBCs) contain haemoglobin proteins that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body (Larson 2016, 240). Each haemoglobin molecule contains four subunits, and each subunit contains a heme group with an iron atom – the binding site for O2 molecules (Honig and Adams 1986, 19).
- RBCs in fresh blood samples from fish, amphibians, reptiles and birds are nucleated (Claver and Quaglia 2009), but mammal RBCs do not have nuclei or any other cytoplasmic organelles at maturity (Telen 2009, 126).
Identification
- RBCs vary in shape, depending on the animal. Nonmammalian RBCs are oval, whereas the morphology of RBCs seen in fresh mammalian blood takes the form of flattened biconcave discs (discocytes).
- Adult human RBCs have an average diameter of about 7.2-7.4 μm (Price-Jones 1933) and a maximum thickness of 2.2 μm (Smith and Wilson 2001). Most animal RBCs fall within 5-10 μm in diameter (Seaman 1975, 1183).
- While the 'mud-cracked' appearance of blood films is often used as an identifiable feature (Langejans and Lombard 2015, 208), other processes can also create a similar effect on stone. Soil and iron oxide deposits displaying a mud-cracked appearance can also be found on archaeological stone tools, even after washing. Thus, it was not possible to securely identify blood films with reflected VLM on the basis of visual characteristics alone.
Identification notes
- It seems reasonable to expect a number of morphological changes to animal RBCs once they are outside the body as residues on stone. We know that upon dehydration or placement in a hypertonic solution, normal RBCs are altered – cell structure changes, becoming shrivelled and crenated (an RBC morphology called an echinocyte that has many evenly spaced projections) (Bain 2006, 91; Nikinmaa 1990, 72; Reinhart and Chien 1986, 1111; Telen 2009, 127). The diameter of fresh human RBCs begins to decrease in the presence of air after only a day (Liao et al. 1998, 193), and a recent study on the microtaphonomy of blood in parietal bone by Cappella et al. (2015) found RBCs were morphologically distinct for only a week after death of the individual. In the archaeological bone Cappella et al. (2015) tested, RBCs were not detected by either: 1) histological staining and subsequent microscopic viewing or 2) immunohistochemical testing with Glycophorin A. Thus, we presume RBCs on experimental stone tools will change at least to some degree in morphology and size as they dry out. Damage to RBC morphology and size will also occur in a water-saturated environment, since RBCs placed in a hypotonic solution undergo transformation, including swelling and becoming first more cup shaped (stomatocytes), then spherical (spherocytes), then hemolysis occurs (Telen 2009, 127).
- SEM work by Hortolà (1992; 2001; 2002) of recent and aged blood films on stone substrates identified specific mammalian RBC morphologies, described as negative replica impressions and moon-like shapes of RBCs. Hortolà (2005) found intact human RBCs within blood films applied to two experimental stone substrates and dried for 1.5 hours. RBCs were apparent at 1000x magnification, using a traditional SEM in low-vacuum mode, without coating the residue (Hortolà 2005).
- Dark brown fungal spores on a common reed (Phragmites australis) leaf residue from the reference collection were found to resemble RBCs in shape and size, and occurred in chains. Barton (2009, 135) also reported the presence of circular fungal bodies surrounding starch on an experimentally buried starch on a stone replica tool; these were of similar size, appearance, and chain formation to the fungal spores observed in our reference collection. The examples of fungal bodies reported by Barton (2009, 135) and those in the reference collection are likely to be conidia spores in chain formation, a common contaminant of archaeological residues described by Haslam (2006b).
Reference residue
- Although isolated blood was not a specific category of residue tested in the current experiment, it was present on all flakes used on beef muscle, fish, bird, and especially on flakes used to cut squirrel.
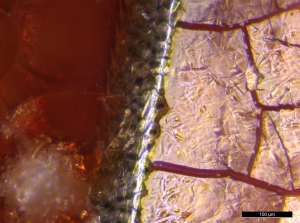
- The fish, bird, and squirrel were frozen prior to being received for use in the experiment. Freezing causes lysis of the cell membranes of RBCs (Lovelock 1953; Nei 1981; Sowemimo-Coker 2002, 47). Unsurprisingly, no intact individual cellular components of any shape (such as discocytes, echinocytes, spherocytes, or variants thereof) could be located in the fish, bird, or squirrel residue suites using up to 1,600x magnification with reflected VLM and up to 1,800x with variable pressure SEM. Rather, ruptured red blood cell membranes, sometimes called 'ghosts' in the literature (Pribor 1971), were present (see Figures 47-49).
- Large red blood films (without identifiable blood cells) were present on the reference collection flint used on the squirrel. The mud-cracked appearance of blood films in the reference collection was maintained despite the squirrel being previously frozen. Flakes that were buried exhibited obvious blood films prior to burial, but decayed completely following burial under every condition and over every time interval tested.


Animal fat
Biological description
- In all animals (the Metazoa), long-term lipid storage occurs in specialised cell types, but adipose tissue formation is only found in the vertebrates (Birsoy et al. 2013, 1541), including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.
- The vertebrates store lipids in a semi-liquid state as triacylglycerol and cholesterol esters (Birsoy et al. 2013, 1543) in fat cells or adipocytes.
- White adipose tissue is found in the abdominal and subcutaneous regions of birds, mammals (Azeez et al. 2014, 4), and some fish (Pond 2011, 230). Amphibians, reptiles, and most fish, store fat intra-abdominally, and have essentially no subcutaneous fat storage (Azeez et al. 2014, 4; Birsoy et al. 2013, 1544).
- In addition to white adipose tissue, mammals also have brown adipose tissue (Pond 2011, 227). Brown adipose tissue has a thermoregulatory function and is found only in mammals (Klingenspor and Fromme 2011, 40). The adipocytes that make up the white adipose tissue are unilocular, or composed of a single compartment, and brown adipose tissue occurs in a multilocular, or multi-compartmentalised arrangement (Cinti et al. 2001). In prepared slides, individual adipocytes are visible at low magnifications (2.5x) (Cinti et al. 2001, 21).
Identification
- Animal fat has previously been identified by a greasy shiny appearance, the fat cells described as globules or ovoid in shape, and forming amorphous smears when crushed (Lombard 2004; 2008, 38, 39).
- Animal fat has been described as white, clear, opaque, yellow, pink to red (marrow), and sometimes bluish in cross-polarised light (Langejans 2009, 65).
- Animal fat residues lack diagnostic structure and individual adipocyte cells are not recognisable on stone tools, possibly owing to crushing and lysis of cell membranes.
- Plants, like animals, also store lipids as triacylglycerols (Murphy 1993, 247; 2001, 365), and plant oil and wax residues cannot be differentiated from animal fat residues on stone tools using only reflected VLM.
- Archaeological animal fat residues are impossible to identify securely on the basis of visual inspection, but extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) may allow the detection of lipids.
Reference residue
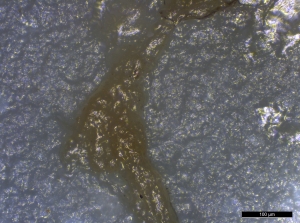
- Even in the fresh, non-degraded reference collection residues, no diagnostic features were present to allow identification. No individual adipocytes could be isolated from the suites of residues examined (such as the fish, goose, squirrel, or beef steak muscle) and identified as white or brown fat cells (Figure 50).
- Examination of potential fat residues with SEM did not reveal any micromorphological structures that could be linked with the residue.
Resin
Biological description
- Natural plant resin is a type of plant exudate that is viscous or solid, flammable, and non-water soluble, but lipid or spirit soluble (Langenheim 2003, 45).
- Secreted tree resin seals injuries from wind, fire, lightning, and herbivory, and prevents invasion of fungi and insects.
Identification
- Only a suggestion of resin is possible based on its amorphous morphology. Resin can appear as shiny droplets or exhibit a rough texture.
- Natural resins appear translucent when fresh and can appear yellow, orange, red, or brown, but upon hardening are often opaque.
Reference residue
- Conifer tree resin appears granular at low magnifications (160x or less) and shiny and orange at higher magnifications (320x or more) (Figure 51). It is worth noting that while raw pine resin was used in the experiment, other resins will probably exhibit different characteristics in terms of colour and texture.
- The resin still appeared relatively rough in texture and amorphous when examined with SEM (Figure 52).
- Resin residues that were experimentally buried underwent a change in colour from semi-translucent reddish-orange to largely opaque grey/white with only small spots of shiny orange remaining visible.